概念
在python中很多对象都是可以直接通过for语句直接遍历的,比如list、string、dict等序列。
访问序列的时候可以使用序列名[索引]方式 从0一直迭代到序列的最后一个条目。
我们把可以迭代访问的对象称之为 可迭代对象,哪些对象是可以被迭代访问的呢?
迭代器的本质就是位置
我们需要了解迭代器的知识。
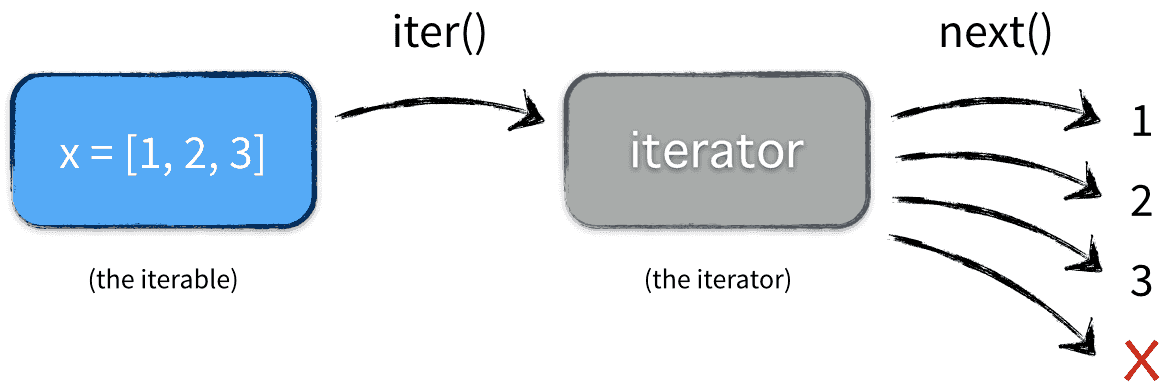
迭代器是容器中的一个成员对象,他实现了迭代器的协议。有两个方法:
- next方法 返回当前迭代器指向的成员(元素),并且将迭代器指向下一个位置
- iter方法 返回迭代器
>>> num = [1,2,3,4,5]
>>> iter(num)
<listiterator object at 0x7fcb6eca44d0>
>>> n = iter(num) #获取到num list容器对象的迭代器
>>> n.next()
1
>>> n.next()
2
>>> n.next()
3
>>> n.next()
4
>>> n.next()
5
>>> n.next()
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
StopIteration
next方法
next(iterator[, default])
Return the next item from the iterator. If default is given and the iterator
is exhausted, it is returned instead of raising StopIteration.
next()方法返回容器的下一个元素,在结尾时引发StopIteration异常。
iter方法
iter(collection) -> iterator
iter(callable, sentinel) -> iterator
Get an iterator from an object. In the first form, the argument must
supply its own iterator, or be a sequence.
In the second form, the callable is called until it returns the sentinel.
获取到一个指定序列或者可迭代对象的迭代器,对于可迭代对象来说可使用iter方法来获取迭代器。
可迭代对象
大部分容器都是可迭代的,另外还有一部分对象也是可以迭代的。比如文件对象。
可迭代对象可以使任意类型的对象,可能不是容器,只要这个对象能够提供迭代器。
iter获取迭代器
>>> s = 'gun'
>>> iter(s)
<str_iterator object at 0x000000BF182A7CF8>
使普通类型的对象成为可迭代对象
一般实现以下两个方法,iter()以及next()方法,iter()方法返回self本对象的迭代器。
实现一个特殊函数iter,此函数要求返回一个iterator对象,对于iterator对象的要求就是实现特殊函数 next,所以一般的做法就是类同时实现iter和next,然后在iter中返回自己。next函数要求依次 返回需要迭代的项目,结束后raise stopiteration。
from collections import Iterator,Iterable
>>> class a(object):
lst = []
index = 0
def __init__(self):
self.lst = [1,2,3,4,5,7]
print ('call init')
def __next__(self):
self.index += 1
if self.index < len(self.lst):
return self.lst[self.index-1]
else:
raise stopiteration
def __iter__(self):
return self
>>> aa =a()
call init
>>> for ii in aa:
print (ii)
1
2
3
4
5
>>> isinstance(aa,Iterable)
True
判断对象是否是可迭代
>>> from collections import Iterable
>>> isinstance(s,Iterable)
True